In a document sent to localities, the Department of Livestock and Veterinary Medicine (Ministry of Agriculture and Environment) sent a document providing information about the Nipah virus.
Accordingly, the Nipah virus (NiV) is a pathogen of the Paramyxoviridae family, Henipavirus genus, which is closely related to the Hendra virus. The natural reservoir of the virus is a fruit bat of the Pteropus genus (horse bat), with the ability to excrete the virus through urine, saliva and feces. This is a disease with a very high mortality rate in humans, ranging from 40 to 75%.
The Nipah virus disease first broke out strongly in Malaysia in 1998, mainly in pigs and spread to farmers. Later, Singapore recorded infections in 1999 in slaughterhouse workers due to contact with imported pigs from the epidemic area.
Although only 5 countries have officially announced human cases, the presence of the Nipah virus in the Pteropus bat population has been detected in many other countries such as Thailand, Cambodia, Indonesia, Ghana and Madagascar. This shows the potential risk spreading throughout Southeast Asia, including Vietnam.
The Nipah virus is mainly transmitted from fruit bats to humans through direct contact with secretions, feces or contaminated food. In addition, the virus can also be transmitted through intermediate hosts, in which pigs play the role of "amplified hosts", spreading to humans when close contact or through respiratory droplets. Many other animal species such as buffaloes, cows, goats, horses, dogs, and cats are also susceptible to the virus. In particular, the disease can be transmitted from person to person through respiratory secretions, especially in the family environment and medical facilities.
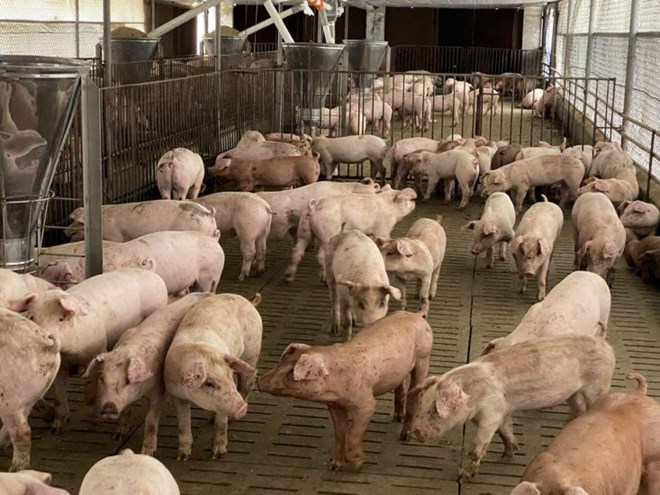

Faced with this situation, the Department of Livestock and Veterinary Medicine proposed that the Departments of Agriculture and Environment of provinces and centrally-run cities proactively implement measures to prevent Nipah virus from entering Vietnam. The focus is to strengthen proactive monitoring at pig farms and households, especially in areas with high fruit bat density or near nature reserves; closely monitor pig herds with abnormal respiratory or neurological manifestations and promptly report and take RT-PCR testing samples when suspicious.
The work of slaughtering control and pig transport quarantine is required to be tightened, not allowing pigs of unknown origin to enter the supply chain. Participants in slaughtering, transporting and contacting animals must strictly comply with personal hygiene regulations.
Local agricultural sectors also need to guide farmers to practice biosafety farming in a practical way, from installing nets to prevent bats and birds from entering, ensuring that food and drinking water sources are not contaminated with wild animal waste, to managing the livestock environment, clearing bushes, and not planting fruit trees to attract bats right next to barns. The limitation of contact, not allowing strangers and unsanitary and disinfected vehicles to enter and exit the farming area is also emphasized.
In addition, it is required to strengthen inter-sectoral coordination in monitoring, detecting, diagnosing, testing and communicating risks for diseases transmitted from animals to humans, including diseases caused by Nipah virus. Communication work needs to focus on raising community awareness about the level of danger and routes of transmission from wild animals to livestock and humans, recommending people to strictly implement the "5 no's" principle: not raising, transporting, illegally trading wild animals; not hunting, slaughtering; not using, consuming wild animal meat; not allowing livestock to come into contact with wild animals; and not concealing epidemics.
When detecting livestock showing abnormal signs or the phenomenon of birds and bats dying en masse, people are not allowed to arbitrarily handle or sell them for sale, but must immediately report to local authorities or veterinary agencies to take samples and handle them according to regulations.